Simple Insights About Transformer Model
This is a brief introduction to transformer that simplifies the model’s structure to help build a quick understanding of what it is trying to realize. The original blogs and video where I learned about it have been posted below.
Links to the reference
- The Illustrated Transformer (A detailed introduction to Transformer)
- Introduction to the Mechanics of Seq2seq Models With Attention
- Brief Introduction to RNNs (Recurrent Neural Networks)
Quick Overview
Transformer is a framework used in Natural Language Processing to help texts translation and generation. Basically, it utilizes a mechanism called Attention and the Recurrent Neural Network to work. Don’t hurry to figure out what they are if you are confused about these two terms. I’ll give necessary explanation to them when it comes to the concrete process in Transformer.
The Workflow of Transformer
Let’s restrict our explanation under the topics of language translation. In this case, we input a sequence of words (namely sentence) into the transformer model and get the output of a sequence of words in another language.
The entire procedure in the model could be divided into 2 parts: Encoding and Decoding.
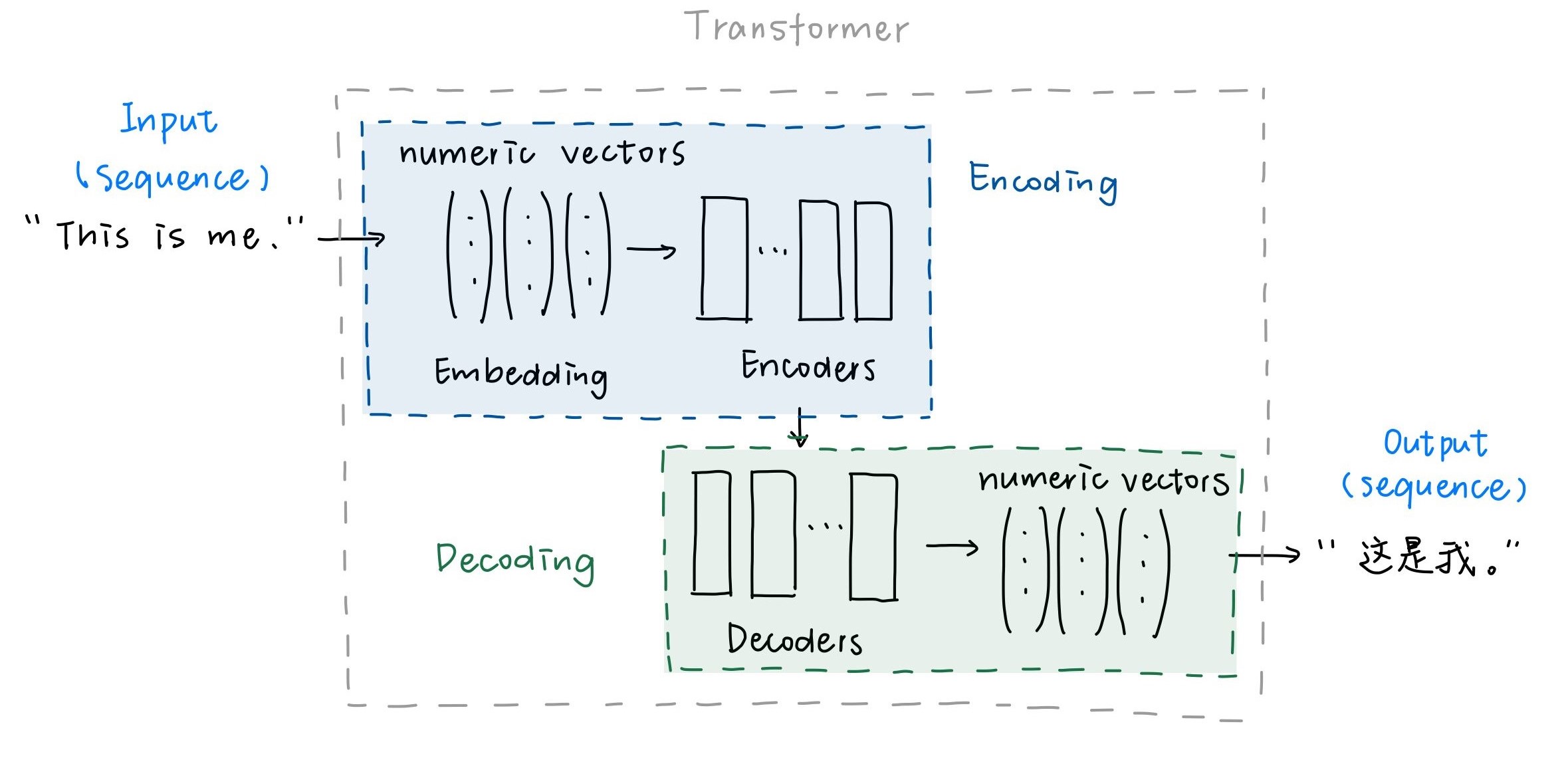
- Encoding
1. Word Embedding
- Transfer the input sequence into numerical vectors.
The calculation in the model should be implemented with mathematical methods, so it’s a necessity to transfer the natural language into numerical forms.
2. Processing vectors through the encoders
- Encode the input sentence with those vectors to capture the meaning of the each single word and the connection between different words.
This is the procedure when the computer is trying to percieve the text. Though during the word embedding, the similarities in meaning of words have been considered, in the encoding part, we are trying to grab the link between words in the given sentence.
The method to capture the features is the Attention mechanism and RNNs.
Attention means when processing a specific word in the input sequence, we generate a vector to denote the influence of each word in the entire sentence on the one being processed. The vectors will be passed to the following decoding process, unveiling how much attention we should pay to other words in the input aside from the one we are trying to decode. So we can simply percieve the Attention as weighted average of the elements in the input sequence.
The way we process the sequence is element by element. However, as we all know the semantic meaning is continous throughout the sequence. The feature of words are expected to generate based on the last words and update considering the following words. So when going through the neural networks, what we need is not only the current word being processed, but also the feature captured of the last word. The neural network that takes both additional information and the output it generated as input is called recurrent neural network.
Based on the RNNs with Attention, we get the encoding results of the input sequence. Then we pass it to the next stage decoding.
- Decoding
1. Processing through the decoders
- Decode the result of the Encoding, give the translation of the words in the input sequence to other numerical vectors oriented to the language we want to translate into.
As we take advantage of the attention mechanics, when decoding a specific vector, we are able to pay attention to other semantically related words in the intial sequence so that the model could perform better.
2. Vocabulary mapping
- Transfer the output numerical vectors in the Decoding into words in the objective language.
First we map the output vectors into the vectors that have the same dimensions as the embedded words in the objective language, so that we can calculate the probabilities of word candidates. When training data, we use supervised method to optimize the loss funciton to give a prediction of the translated sentence. So we expect the model to predict the correct words based on the probability it calculates for the mapped vectors.
